Self tapping screw
Hexagonal head tapping screws are a type of mechanical component. Self tapping screws are commonly used for connecting thin metal plates (steel plates, saw plates
Generally, it refers to pointed, coarse toothed, and hard wood screws, as well as aluminum alloy and plastic screws. A special self tapping screw used for threading metal holes is called a tap.
Self tapping screws are used for non-metallic or softer metals without the need for bottom holes and tapping; Self tapping screws are pointed, which is the only way to "self tap"; Ordinary screws are flat headed and of uniform thickness.
Self tapping screws refer to holes drilled without the need for tapping teeth, and the screws used are different from ordinary ones. The head is pointed, with a relatively large pitch, similar to a chip free tap, and can be directly screwed in without tapping teeth. This method is commonly used for metals and plastics.
It can use its own threads to "drill, squeeze, and press" the solidified material onto the corresponding threads, making them closely fit each other.
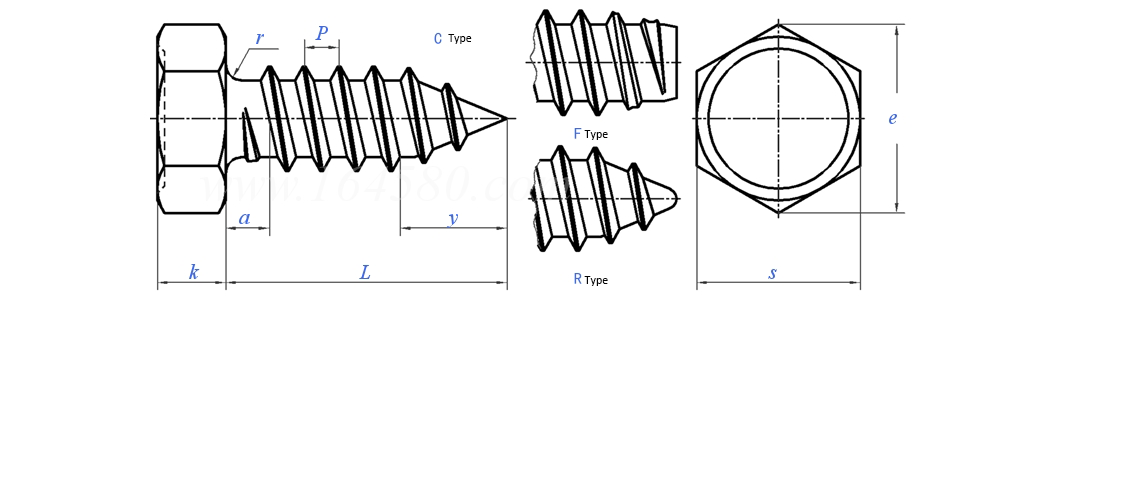
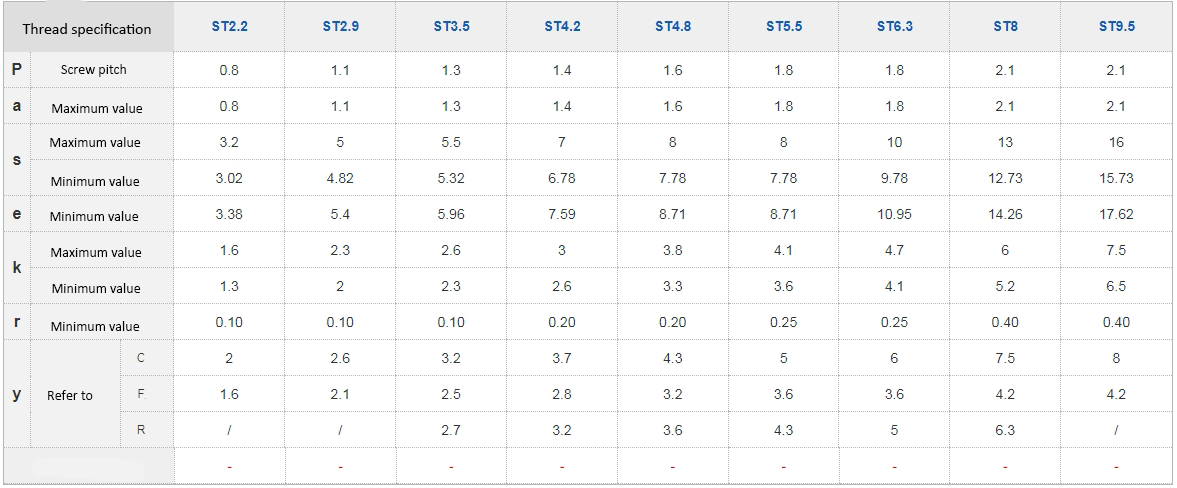
Self tapping screw is a type of screw with a drill bit, which is constructed using specialized electric tools, and is drilled, threaded, fixed, and locked in one operation. Self tapping screws are mainly used for the connection and fixation of some relatively thin parts, such as the connection between color steel plates and color steel plates, the connection between color steel plates and purlins, wall beams, etc. Their penetration capacity generally does not exceed 6mm, and the maximum does not exceed 12mm. Self tapping screws are often exposed outdoors and have strong corrosion resistance; Its rubber sealing ring can ensure that there is no water leakage at the screw and has good corrosion resistance. Self tapping screws are usually described by three parameters: screw diameter series, number of threads per inch length, and screw length. There are two types of screw diameter levels: 10 and 12, with corresponding screw diameters of 4.87mm and 5.43mm, respectively; There are three levels of threads per inch length: 14, 16, and 24. The more threads per inch length, the stronger its self drilling ability.
Thread forming
Thread Forming Tapping Screws - Developed directly from sheet iron screws, thread forming self tapping screws require pre drilling and then screwing the screws into the holes to forcefully extrude and fit the female threads. The material originally in the female thread position will be squeezed between the male threads, which is called thread forming self tapping screws. It can only be applied to thin and plastic materials, therefore it has been developed; Thread Cutting Tapping Screws - Cut one or more cutting edges at the end of the thread, allowing for the use of the screw tail and teeth to cut mating female threads in a similar manner to a screw tap when pre drilling. It can be used in materials that are difficult to shape, such as thick boards, relatively hard or fragile materials.
Thread rolling
(Thread Rolling Tapping Screws) - Triangular self tapping screws, also known as Type TT (Type Tai still has a patent), are developed based on the principle of forming screw taps. Thread rolling self tapping screws have a specially designed thread and tail end that allow the screw to roll into a matching female thread under intermittent pressure. At the same time, the material around the hole can more easily fill the space between the thread and the tooth base of the self tapping screw, Due to its smaller friction force compared to threaded self tapping screws, it can be used on thicker materials, with better torque control for rotation and higher strength after combination. The engineering standard definition of thread rolling self tapping screws is higher and clearer in terms of material, heat treatment, and strength compared to forming or cutting self tapping screws, making thread rolling self tapping screws a true "structural" fastener
Surface Treatment
Surface treatment of self tapping screws: Most of the surface coating of self tapping screws is coated with zinc plating or zinc phosphate. Cadmium plating is rarely used due to its high cost and toxicity. If appearance is important, nickel or chromium plating can be chosen. There are two issues with appearance treatment: firstly, appearance treatment not only increases the scale (such as reducing pores), but also affects the connection between torque, tightening degree, and strength. Therefore, when conducting penetration experiments, different rules must be followed for galvanizing, cadmium plating, or phosphate plating. When testing the applicable drilling hole diameter, the screws used must be screws with the same surface treatment. The second reason is that high hardness, small-scale self tapping screws often fail to be used due to hydrogen embrittlement. Self tapping screws have to be carburized in order to penetrate into the iron plate. After carburization treatment, high hardness and high carbon content will occur, and hydrogen embrittlement will occur when electroplating or pickling treatment is carried out in this situation. The recommended method for eliminating hydrogen embrittlement in regulations is: a). Bake within 1 hour after electroplating or pickling treatment. b). Temperature: 375-425 ° F (190-220 ° C). Time: At least 4 hours. Hydrogen embrittlement test: The hydrogen embrittlement test mainly tests whether there is residual hydrogen in the screw arrangement of the self tapping screw and whether it will cause embrittlement of the self tapping screw. (Generally, brittle fracture does not occur in a short period of time, and certain stress must be applied to show it) Electroplated or coated screws should be installed in the test iron plate and steel flat washer according to the rules in Table 3. The standard flat washer should be used for the lower bearing surface of the outstanding head type screw head, The countersunk (Oval) screw uses a matched steel plate with chamfer distance. The thickness of the flat washer or distance piece installed on the lower bearing surface of the head should be able to fit the maximum ineffective tooth length of the screw. Regarding the long screws with half teeth, their handles can be supported by longer cold-rolled steel distance pieces or flat washers to ensure that the complete tooth part can be formed and maintained within the thickness of the test iron plate. The screw should be locked to 80% of the maximum breaking torque. The breaking torque is determined by locking 5 screws until they break at their average value. After continuing to lock for 24 hours, the screw should be loosened and then turned back to the original locking torque. The screw should have no significant failure.