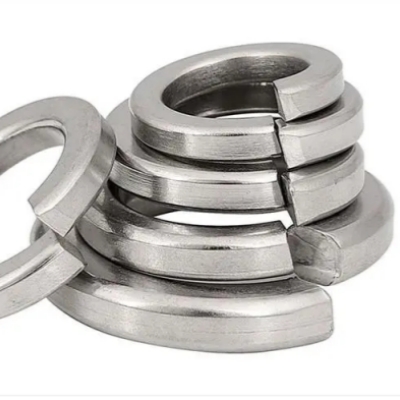
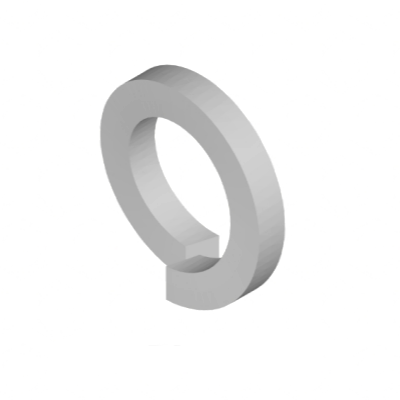
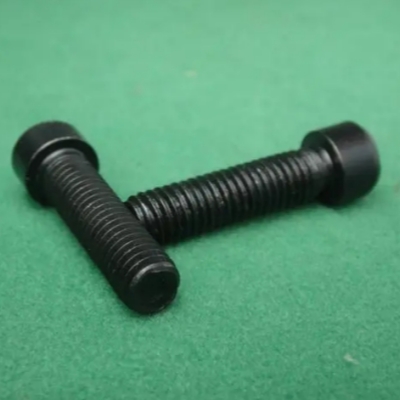
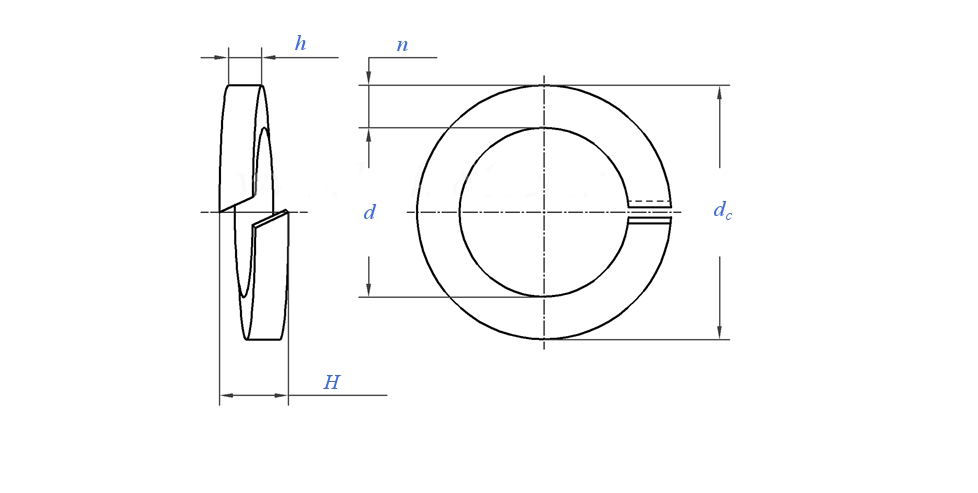
Spring washers are widely used in load-bearing and non load-bearing structures of general mechanical products, characterized by low cost, easy installation, and suitability for frequently disassembled parts.
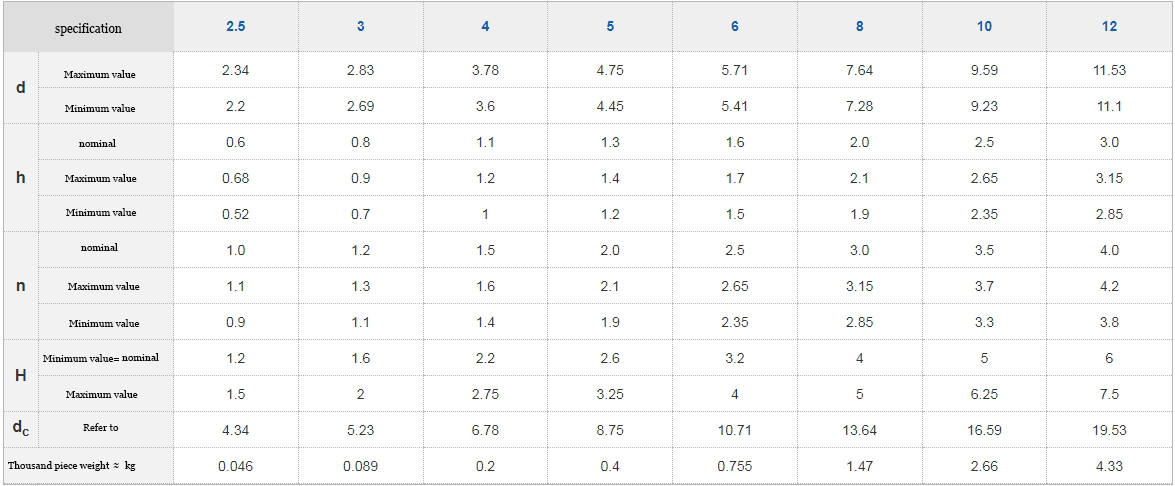
The materials of spring washers include stainless steel and carbon steel, and carbon steel is also known as iron. The commonly used spring washer specifications and sizes include M3, M4, M5, M6, M8, M10, M12, M14, and M16. The national standard GB/T 94.1-2008 for spring washers specifies the technical conditions for elastic washers with specifications ranging from 2-48mm
Usually, 65MN spring steel or 70 # carbon steel, 3Cr13, stainless steel materials SUS304 or SUS316, and phosphorus bronze materials can also be used.
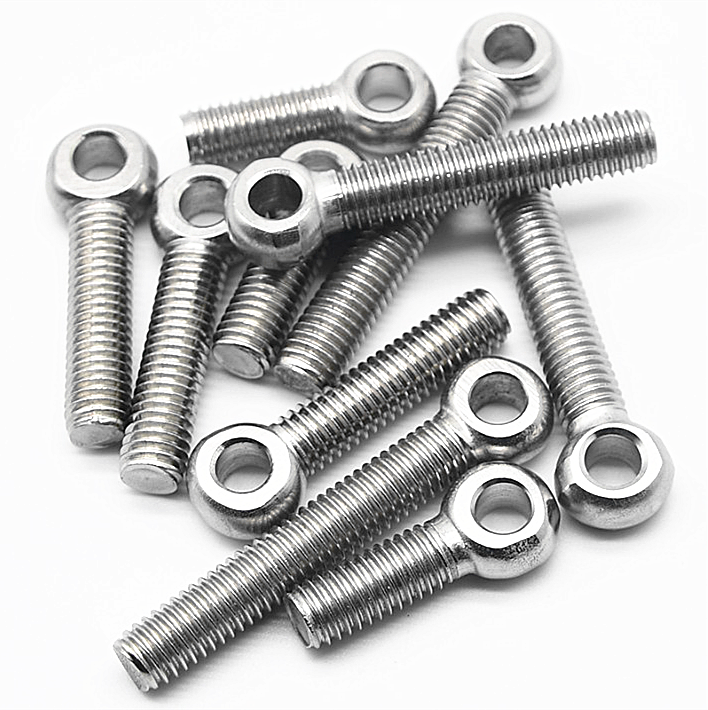
Spring washers are used to prevent loosening. For example, the bolts connecting the motor to the base usually need to be equipped with spring washers, because if there is no spring washer during motor vibration, the nut will loosen. Generally, fasteners on equipment with vibration are equipped with spring washers, and flanges generally do not require washers. The addition or absence of spring washers on the flange is related to the medium flowing through the pipeline. If it is easy to generate pulses, it is best to add spring washers. There are also high-speed fluid pipelines with frequent changes in diameter, so do not generalize. On some valves, spring washers are required to be added to the packing box gland flange, and the selection of spring washers is included in the automatic selection.
Spring washers can play a role in preventing loosening and increasing pre tightening force, while flat washers do not have this function. They can be used to increase the tightening contact area, prevent friction between bolts and workpieces, protect the surface of connecting parts, and prevent scratches on the surface of workpieces when bolts and nuts are tightened.
But for some important connections, such as those that rely mainly on compression to generate friction and transmit power, spring pads cannot be used. Using them will reduce the rigidity of the connection and may lead to accidents. When the strength of the connected parts is low, flat washers or flange bolts are used to increase the contact area. When there is vibration, pulse, or significant temperature fluctuations in the medium, spring washers must be used.
The cause of fracture
1. The phenomenon of expansion of the spring washer is generally not a problem with the spring washer itself.
2. The spring washer that undergoes expansion must be subjected to a radial outward tension, which originates from the tightening axial force generated by the tightening torque.
3. The outer chamfer of the nut support surface generates a radial component of the axial clamping force, which causes the opening of the spring washer to expand. The smaller the chamfer diameter, the greater the possibility of bulging.
Adding a flat washer between the nut and spring washer can help slow down or prevent the occurrence of ring expansion, but a flat washer that is too thin or too soft cannot prevent ring expansion.
5. The reasons for hydrogen embrittlement and fracture of spring washers are generally due to unreasonable heat treatment processes, as well as failure to undergo hydrogen removal treatment in a timely manner after electroplating zinc.
A large number of experiments and long-term practical experience have confirmed the above analysis.